Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Epidemiol Health > Volume 41; 2019 > Article
-
Original Article
Evaluating maternal and child health indicators for the Sustainable Development Goals in 2018: what is Iran’s position? -
Elham Khatooni1
 , Isa Akbarzadeh1
, Isa Akbarzadeh1 , Elham Abdalmaleki2
, Elham Abdalmaleki2 , Zhaleh Abdi2
, Zhaleh Abdi2 , Elham Ahmadnezhad2
, Elham Ahmadnezhad2
-
Epidemiol Health 2019;41:e2019045.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4178/epih.e2019045
Published online: October 11, 2019
1Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
2National Institute for Health Research, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
- Correspondence: Elham Ahmadnezhad National Institute for Health Research, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, 70 Bozorgmehr Street, Tehran 1416833481, Iran E-mail: ahmadnezhad@tums.ac.ir
©2019, Korean Society of Epidemiology
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Iranian women's birth experiences: a cross-sectional study
Mona Ghobadi, Farzaneh Pazandeh, Barbara Potrata, Ehsan Kazemnejad Lili
British Journal of Midwifery.2022; 30(12): 685. CrossRef - Sanctions on Iran and their impact on child health*
Yasmin Madani-Lavassani
Medicine, Conflict and Survival.2020; 36(4): 359. CrossRef


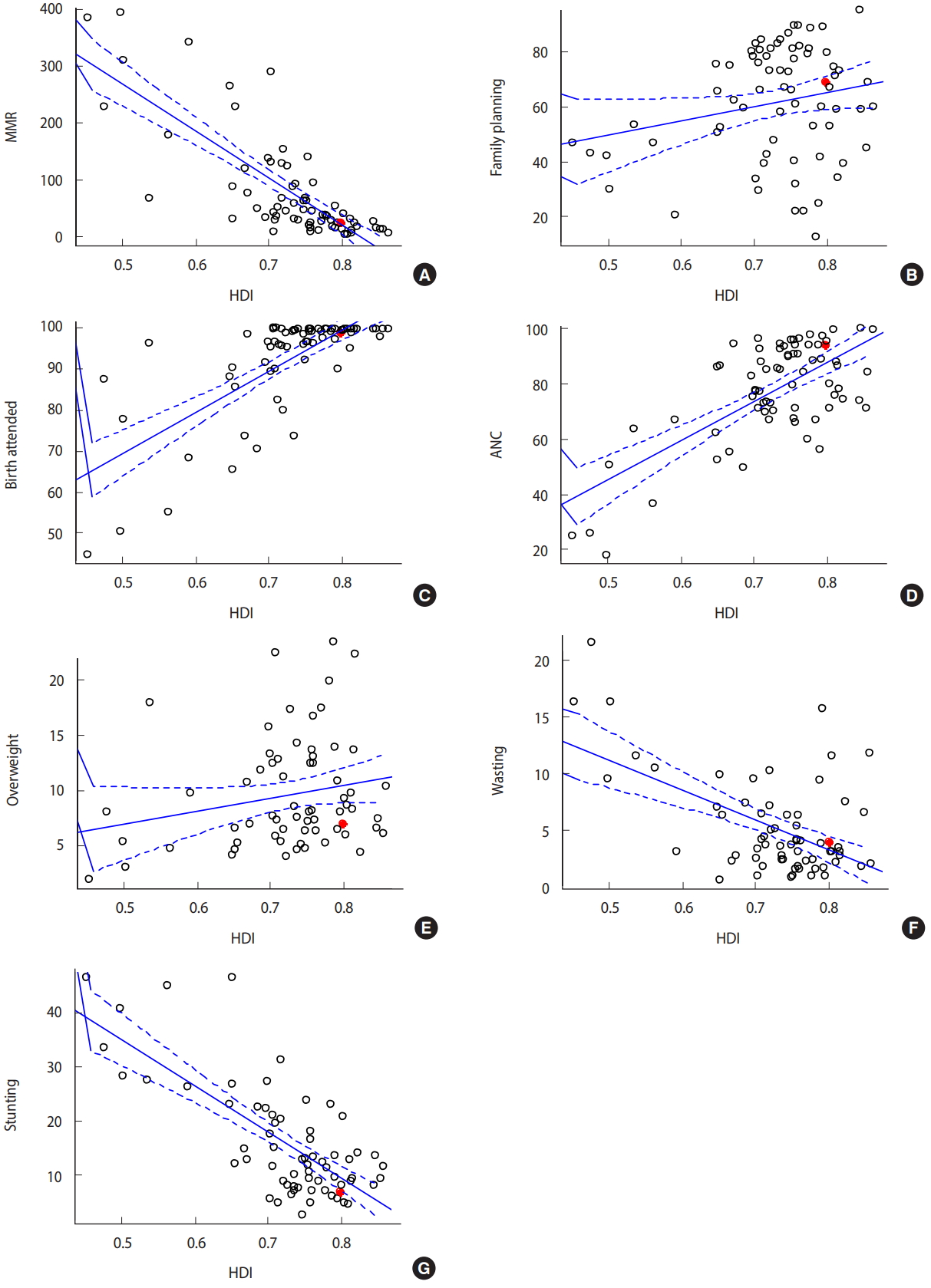
Figure 1.
Figure 2.
| Subject | Indicator | Target for 2030 or definition | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maternal mortality | 3.1.1: Maternal mortality ratio | 3.1: Reduce the global maternal mortality ratio to less than 70 per 100,000 live births | 2015 |
| Skilled birth attendance | 3.1.2: Proportion of births attended by skilled health personnel | 3.1: Reduce the global maternal mortality ratio to less than 70 per 100,000 live births | 2002-2016 |
| Child mortality | 3.2.1: Under-five mortality rate | 3.2: End preventable deaths of newborns and children under 5 yr of age, with all countries aiming to reduce neonatal mortality to at least as low as 12 per 1,000 live births and under-five mortality to at least as low as 25 per 1,000 live births | 2017 |
| 3.2.2: Neonatal mortality rate | |||
| Hepatitis B incidence | 3.3.4: Hepatitis B incidence per 100,000 population | 3.3: By 2030, end the epidemics of AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria, and neglected tropical diseases and combat hepatitis, waterborne diseases, and other communicable diseases | 2015 |
| Family planning | 3.7.1: Proportion of women of reproductive age (aged 15-49 yr) who have their need for family planning satisfied with modern methods | 3.7: Ensure universal access to sexual and reproductive health care services, including for family planning, information and education, and the integration of reproductive health into national strategies and programs | 2007-2016 |
| Child immunization | One-yr old children who have received 3 doses of DTP3 (%) | DTP3, which is identical to coverage with the pentavalent vaccine in most countries, is an indicator of a routine infant immunization system; However, several other vaccines, such as for those measles (second dose), pneumococcal pneumonia, and rotavirus diarrhea, typically have lower coverage, and the fraction of children receiving all vaccines in a national schedule is typically much lower (although not possible to measure directly with existing data systems in most countries); This indicator could be replaced with a second dose of measles vaccine, following the recent recommendation of the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization | 2017 |
| Pregnancy and delivery care | ANC, four or more visits 4 (%) | No. of ANC visits captures contact with the health system but it does not capture quality of care received and may not lead to improved mortality outcomes | 2002-2016 |
| Child treatment | Care-seeking behavior for children with suspected pneumonia (%) | Pneumonia is a leading cause of child illness and death; Suspected pneumonia is determined based on a series of survey questions about illnesses in the past two weeks, which may include mild respiratory illnesses; The indicator does not currently capture the quality of care received, as parental recall of treatment specifics tends to be poor | 1993-2016 |
| Stunting among children | 2.2.1: Prevalence of stunting (height for age <-2 SD from the median of the WHO Child Growth Standards) among children under 5 yr of age | 2.2: By 2030, end all forms of malnutrition, including achieving, by 2025, the internationally agreed targets on stunting and wasting in children under 5 yr of age, and address the nutritional needs of adolescent girls, pregnant and lactating women and older persons | 1995-2016 |
| Wasting and overweight among children | 2.2.2: Prevalence of malnutrition (weight for height >+2 SD or <-2 SD from the median of the WHO Child Growth Standards) among children under 5 yr of age, by type (wasting and overweight) | 2.2: By 2030, end all forms of malnutrition, including achieving, by 2025, the internationally agreed targets on stunting and wasting in children under 5 yr of age, and address the nutritional needs of adolescent girls, pregnant and lactating women and older persons | 1989-2016 |
| Indicator | World mean (World Bank) | Total median | Weighted mean |
Iran | Best | Worst | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper middle-income | Eastern Mediterranean | Outlook Document | ||||||
| Maternal mortality | 216.00 | 40.00 | 36.90 | 161.49 | 121.59 | 25.00 | Belarus and Kuwait (4.00) | Somalia (723.00) |
| Skilled birth attendance | 80.01 | 97.85 | 98.43 | 70.62 | 78.24 | 99.00 | Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan (100.00) | Somalia (9.40) |
| Child mortality | 40.80 | 16.00 | 12.11 | 23.41 | 40.23 | 14.90 | Montenegro (3.50) | Somalia (127.00) |
| Hepatitis B incidence | - | 0.37 | 0.61 | 0.81 | 1.23 | 0.02 | Iran (0.02) | Somalia (10.54) |
| Family planning | - | 63.85 | 85.73 | 50.27 | 53.95 | 68.60 | China (95.00) | Albania (12.90) |
| DTP3 coverage | 85.58 | 94.00 | 95.30 | 89.70 | 84.55 | 99.00 | 16 countries (99.00) | Equatorial Guinea (25.00) |
| Antenatal care | 75.00 | 79.50 | 79.55 | 68.18 | 61.56 | 94.00 | Bahrain (100.00) | Somalia (6.30) |
| Care-seeking behavior for children | 60.00 | 73.80 | 74.07 | 64.32 | 62.73 | 75.90 | Djibouti (94.40) | Somalia (13.00) |
| Stunting | 22.20 | 12.70 | 9.99 | 17.62 | 25.97 | 6.80 | St. Lucia (2.50) | Yemen (46.50) |
| Overweight | 5.60 | 7.85 | 7.35 | 7.72 | 7.43 | 6.90 | Yemen (2.00) | Albania (23.40) |
| Wasting | 7.50 | 3.70 | 2.35 | 7.68 | 7.99 | 4.00 | Guatemala (0.70) | Djibouti (21.50) |
| Country | Eastern mediterranean | Upper-middle-income | Outlook Document | Country | Eastern mediterranean | Upper-middle-income | Outlook Document |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afghanistan | O | - | O | Kuwait | O | - | O |
| Albania | - | O | - | Lebanon | O | O | O |
| United Arab Emirates | O | - | O | Libya | O | O | - |
| Armenia | - | O | O | St. Lucia | - | O | - |
| Azerbaijan | - | O | O | Morocco | O | - | - |
| Bulgaria | - | O | - | Maldives | - | O | - |
| Bahrain | O | - | O | Mexico | - | O | - |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | - | O | - | Marshall Islands | - | O | - |
| Belarus | - | O | - | Macedonia | - | O | - |
| Belize | - | O | - | Montenegro | - | O | - |
| Brazil | - | O | - | Mauritius | - | O | - |
| Botswana | - | O | - | Malaysia | - | O | - |
| China | - | O | - | Namibia | - | O | - |
| Colombia | - | O | - | Nauru | - | O | - |
| Costa Rica | - | O | - | Oman | O | - | O |
| Cuba | - | O | - | Pakistan | O | - | O |
| Djibouti | O | - | - | Peru | - | O | - |
| Dominica | - | O | - | Paraguay | - | O | - |
| Dominican Republic | - | O | - | Qatar | O | - | O |
| Algeria | - | O | - | Romania | - | O | - |
| Ecuador | - | O | - | Russia | - | O | - |
| Egypt | O | - | - | Saudi Arabia | O | - | O |
| Fiji | - | O | - | Sudan | O | - | O |
| Gabon | - | O | - | Somalia | O | - | - |
| Georgia | - | - | O | Serbia | - | O | - |
| Equatorial Guinea | - | O | - | Suriname | - | O | - |
| Grenada | - | O | - | Syria | O | - | O |
| Guatemala | - | O | - | Thailand | - | O | - |
| Guyana | - | O | - | Tajikistan | - | - | O |
| Iran | O | O | O | Turkmenistan | - | O | O |
| Iraq | O | O | O | Tonga | - | O | - |
| Jamaica | - | O | - | Tunisia | O | - | - |
| Jordan | O | O | O | Turkey | - | O | O |
| Kazakhstan | - | O | O | Tuvalu | - | O | - |
| Kyrgyzstan | - | - | O | Total | 21 | 56 | 24 |
| Indicator | Rank |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern Mediterranean countries (out of n countries) | Outlook Document countries (out of n countries) | Upper-middle income countries (out of n countries) | |
| Maternal mortality | 8 (21) | 9 (24) | 11 (51) |
| Birth attendance by skilled personnel | 4 (20) | 7 (23) | 9 (54) |
| Child mortality | 9 (21) | 12 (24) | 24 (55) |
| Hepatitis B incidence | 1 (21) | 1 (24) | 1 (55) |
| Immunization coverage | 1 (21) | 1 (24) | 1 (55) |
| Care-seeking behavior for children with an acute respiratory infection | 9 (21) | 8 (24) | 19 (52) |
| Family planning | 5 (21) | 5 (24) | 27 (54) |
| Antenatal care | 4 (21) | 8 (24) | 10 (55) |
| Stunting | 2 (20) | 2 (23) | 9 (50) |
| Wasting | 6 (20) | 8 (23) | 21 (50) |
| Overweight | 8 (20) | 10 (23) | 16 (50) |
| Indicator | Total |
Eastern Mediterranean |
Prospective Outlook |
Upper-middle income |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-value | R | p-value | R | p-value | R | p-value | R | |
| Maternal mortality ratio | <0.001 | -0.787 | <0.001 | -0.861 | <0.001 | -0.852 | <0.001 | -0.728 |
| Birth attendance | <0.001 | 0.721 | <0.001 | 0.715 | <0.001 | 0.784 | <0.001 | 0.664 |
| Child mortality | <0.001 | -0.808 | <0.001 | -0.861 | <0.001 | -0.838 | <0.001 | -0.781 |
| Hepatitis B incidence | <0.001 | -0.419 | 0.002 | -0.639 | <0.001 | -0.710 | <0.001 | -0.484 |
| DTP3 vaccine coverage | <0.001 | 0.573 | 0.001 | 0.705 | <0.001 | 0.681 | <0.001 | 0.550 |
| Antenatal care coverage | <0.001 | 0.683 | <0.001 | 0.850 | <0.001 | 0.770 | 0.039 | 0.248 |
| Care-seeking | 0.003 | 0.346 | 0.049 | 0.445 | 0.016 | 0.485 | 0.045 | 0.282 |
| Family planning | 0.059 | 0.225 | 0.061 | 0.426 | 0.078 | 0.367 | 0.359 | 0.130 |
| Overweight under 5 | 0.095 | 0.209 | 0.494 | 0.167 | 0.212 | 0.271 | 0.203 | 0.189 |
| Stunting under 5 | <0.001 | -0.734 | <0.001 | -0.874 | <0.001 | -0.872 | <0.001 | -0.505 |
| Wasting under 5 | <0.001 | -0.541 | 0.001 | -0.715 | <0.001 | -0.706 | 0.836 | -0.031 |
WHO, World Health Organization; AIDS, acquired immune deficiency syndrome; DTP3, diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis; ANC, antenatal care; SD, standard deviation.
DTP3, diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis.
R, Pearson correlation coefficient; DTP3, diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis.

 KSE
KSE

 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

